After the halving, Bitcoin (BTC) miners will be under pressure as rewards dwindle and costs soar. Can innovative strategies and market dynamics help you remain profitable?
Bitcoin halving is an event built into the Bitcoin protocol that occurs approximately every four years. This results in a reduction in the rewards miners receive for adding new blocks to the blockchain. The latest halving, which occurred in April 2024, reduced the block reward from 6.25 BTC to 3.125 BTC.
This event, which is central to the deflationary nature of Bitcoin, will impact the supply of new Bitcoin and impact the Bitcoin mining industry and the broader cryptocurrency market as a whole, presenting a variety of challenges and opportunities.
In this article, we take a look at the post-halving world and how the Bitcoin mining sector can adapt.
Miner Pressure: Understanding the Challenge
Reward reduction
One of the immediate effects of the halving was a reduction in profit margins for miners. By cutting miners’ block rewards, the halving had a direct impact on miners’ income, as they began receiving fewer coins for their efforts.
At the time of this writing, the dollar value of Bitcoin block rewards was approximately $215,000 and the cryptocurrency price was approximately $68,800 per coin. But before then, Bitcoin mostly traded around $60,000, meaning a typical block reward was worth less than $200,000.
Manthan Dave, co-founder of Ripple-backed cryptocurrency management platform Palisade, said in a conversation with crypto.news that reduced rewards could force smaller, less profitable mining operations to close shop or join other mining operations.
In his opinion, such a scenario could lead to centralization of the Bitcoin network, as the number of participants involved in its operation would be increasing.
“Everyone is feeling the pressure after the halving… We will likely see smaller, less efficient mining devices struggle or collapse. “Consolidation will continue, sparking concerns about centralization.”
Palisade co-founder Manthan Dave
Bitcoin Price Dynamics: Impact on the Mining Ecosystem
After the halving, miners needed the price of Bitcoin to be high for potential profits to justify the significant energy costs associated with mining. In such a case, new miners will be incentivized to join the network, and existing miners may be motivated to expand their operations and improve energy efficiency.
On the other hand, if the price of Bitcoin falls, miners could quickly incur losses, which could force less efficient miners out of the market and reshape the mining sector in the process.
The latest figures from market analytics firm MacroMicro provide a snapshot of the sometimes unsustainable costs of mining. According to their data, the average Bitcoin mining cost as of June 3 was approximately $78,115 compared to the Bitcoin price of $68,804.
This means that the average mining cost relative to the Bitcoin price is around 1.14, which can be interpreted as a slim choice for many BTC mining operations.
According to a recent CoinShare survey, some of the less profitable miners are expected to close. Additionally, some miners are expected to relocate to areas with access to cheaper electricity.
For example, a Bloomberg report dated February 7 found that approximately 21 BTC miners had signed contracts with the Ethiopian government to relocate their operations to the East African country.
increased competition
After a halving event, competition between miners often intensifies as they compete for a smaller reward pool. This means that miners with more efficient operations, access to cheaper energy sources, or economies of scale may have a competitive advantage over their counterparts.
As competition increases, less efficient miners may be pressured to optimize their operations or exit the market altogether.
However, Manthan Dave believes that players in the Bitcoin mining space affected by increased competition will not necessarily leave the sector entirely. He thinks they can refocus their energies on mining and minting other cryptocurrencies.
“Miners leaving the Bitcoin ecosystem for cost reasons are unlikely to leave the cryptocurrency itself.” Dave pointed out. “They are likely to reuse hardware and switch to mining on other chains or reallocate capital to other operations such as staking.”
Adjust network hashrate and mining difficulty
If profit margins fall and some mining operations are shut down or rescheduled, this will invariably affect Bitcoin’s network hashrate. Network hashrate is the total computational power used to mine and process Bitcoin transactions.
Typically, as the price of Bitcoin rises, mining becomes more profitable and the hash rate also increases, attracting more participants and increasing computing power. Conversely, when the hash rate falls, miners shut down their equipment because they can no longer make a profit.
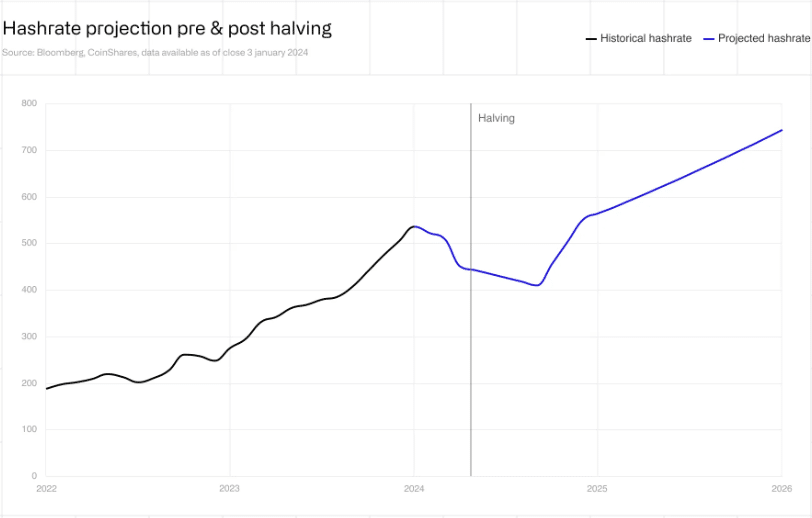
According to Blockchain.com, the current hashrate is 612.99EH/s, which is still lower than the 7-day moving average all-time high of 629.75EH/s recorded in April 2024.
However, the CoinShare report cited earlier predicted that Bitcoin hashrate could reach 700EH/s by 2025.
The Bitcoin protocol usually has a built-in difficulty adjustment mechanism that makes BTC mining harder or easier depending on the prevailing circumstances.
This adjustment occurs approximately every two weeks and is based on how long it took to mine the previous 2016 blocks. Always aim to keep your block times averaging around 10 minutes.
Possible solutions
Jurisdiction Arbitrage
Experts believe that jurisdictional arbitrage, the practice of taking advantage of differences in regulations, laws and costs between different countries or regions, could be a viable strategy for miners looking to optimize their operations.
Manthan Dave, co-founder of Palisade, points out that jurisdictional arbitrage could be an important vehicle for new entrants to the Bitcoin mining sector, given the significant difficulty and capital intensity of starting such an operation.
“Jurisdictional arbitrage is a powerful means of attracting new participants, given that it is already very difficult and capital intensive to get started.” Dave pointed out. “Regulatory clarity in jurisdictions with lower electricity costs could open opportunities for new companies to set up mining operations.”
Different regions offer varying levels of regulatory clarity and incentives, which can influence where miners choose to begin operations. For example, countries with low electricity costs and favorable regulatory environments will be attractive hubs for mining activity following the halving.
Regulatory clarity can also provide significant benefits, including reducing uncertainty and allowing miners to plan for long-term investments.
There has been a noticeable influx of mining operations in places like Texas, Kazakhstan, and the aforementioned Ethiopia, where electricity is relatively cheap and regulatory frameworks are conducive to mining.
Conversely, industry observers expect that tighter regulations and higher energy costs in other regions will force miners to relocate, reshaping the global distribution of mining power in the process.
Diversify and Adapt
Facing pressure from the halving, analysts expect diversification to become a pivotal strategy for miners.
This can take many forms, from expanding into other cryptocurrencies to incorporating additional revenue streams, such as providing cloud mining services or leveraging the excess heat generated by mining operations for other industrial purposes.
For example, some miners, such as Texas-based Lancium, have ventured into renewable energy projects and converted surplus energy into Bitcoin.
Other companies, such as Bitfarms, are exploring vertical integration, encompassing everything from producing mining hardware to setting up dedicated energy facilities.
The key to all these strategies is to not only improve profitability but also contribute to the resilience of mining operations.
Spot Bitcoin ETF: A game-changer in market dynamics
Market observers see the introduction of a spot Bitcoin ETF as having the potential to significantly impact the dynamics around Bitcoin. This product could provide a new avenue for investment and attract institutional investors, ultimately providing a stabilizing effect on the Bitcoin market.
“Spot Bitcoin ETFs are a game changer. This allows institutions and investors to easily hold Bitcoin for long periods of time without having to manage private keys. This consistent buying pressure will counteract the selling pressure from miners, leading to a more stable and bullish Bitcoin market.”
Palisade co-founder Manthan Dave
Moreover, the increased accessibility and legitimacy that ETFs bring could result in reduced volatility, a long-standing problem in cryptocurrency markets. A more stable market could mean better prices and inevitably better profits for miners.
Analysts have also suggested that ETFs could potentially influence investor sentiment, instilling greater confidence and encouraging more capital flows into Bitcoin. This influx of institutional funds can benefit miners as well as investors by providing the liquidity needed to support market stability.
Sharing his insights on this topic, Manthan Dave noted that in the long run, ETFs will increase confidence in cryptocurrencies and reduce volatility in the overall market. He noted that the launch of an Ethereum ETF remains to be seen, which would certainly bring in new capital as Ethereum is more ecologically viable than Bitcoin due to its much lower energy consumption. However, he cautioned that investors are also likely to pull capital from Bitcoin ETFs as they seek diversification.
Rescue rune?
Another interesting post-halving example for BTC miners is the launch of the Runes protocol on the Bitcoin network. Introduced concurrently with the fourth Bitcoin halving event, this protocol helps create fungible tokens on the Bitcoin network using block space more efficiently than the BRC-20 protocol.
This was something of a blessing for BTC miners. The increase in transaction volume resulting from Rune etching helped sustain miners’ profits for some time, with miners earning a total of 2,253 BTC in fees in the first two weeks after Rune’s launch.
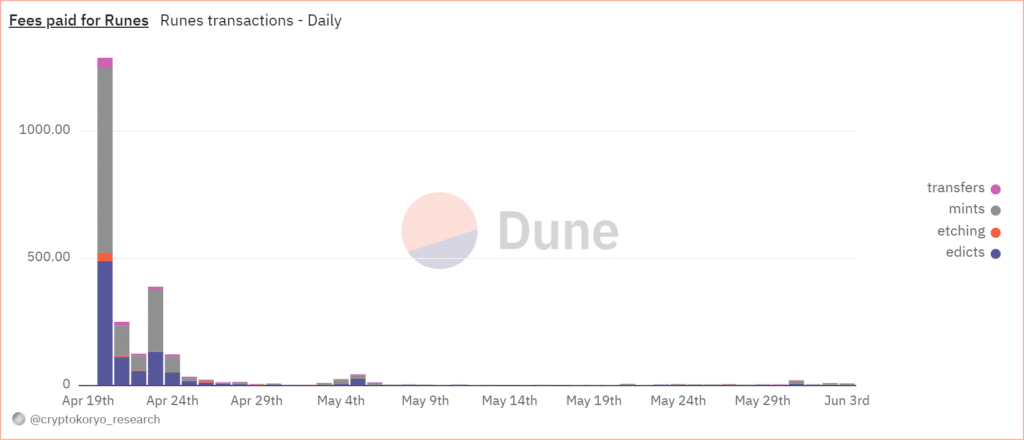
At the time, data from Dune Analytics showed that more than 80% of Bitcoin network transactions involved runes, while actual BTC transactions fell to less than 20% of all transactions.
As the number of transactions increases, network fees increase, which results in more money for miners. However, the windfall appears to have been short-lived, with follow-up figures from Dune showing rune trading numbers continuing to decline.
Predicting the Future: Bitcoin’s Trajectory
Predicting Bitcoin’s price trajectory after its halving requires analyzing various market trends and factors. Historically, the price of Bitcoin has experienced significant increases following halvings due to decreased supply and increased demand.
However, the current environment presents unique challenges, including macroeconomic factors and an evolving regulatory environment. Industry experts have offered varying perspectives on the future of Bitcoin.
Some predict continued growth driven by increased adoption and technological advancements. Others warned of potential risks, such as regulatory crackdowns or market saturation.
Nonetheless, the long-term outlook for Bitcoin and its mining ecosystem remains optimistic, with experts like Manthan Dave predicting the BTC price to approach $100,000 before 2025.
“Looking at what’s to come, there’s a good chance Bitcoin will hit $100,000 by the end of this year.” predicted the Palisade co-founder.

